P-Chain
A review of the Platform Chain.
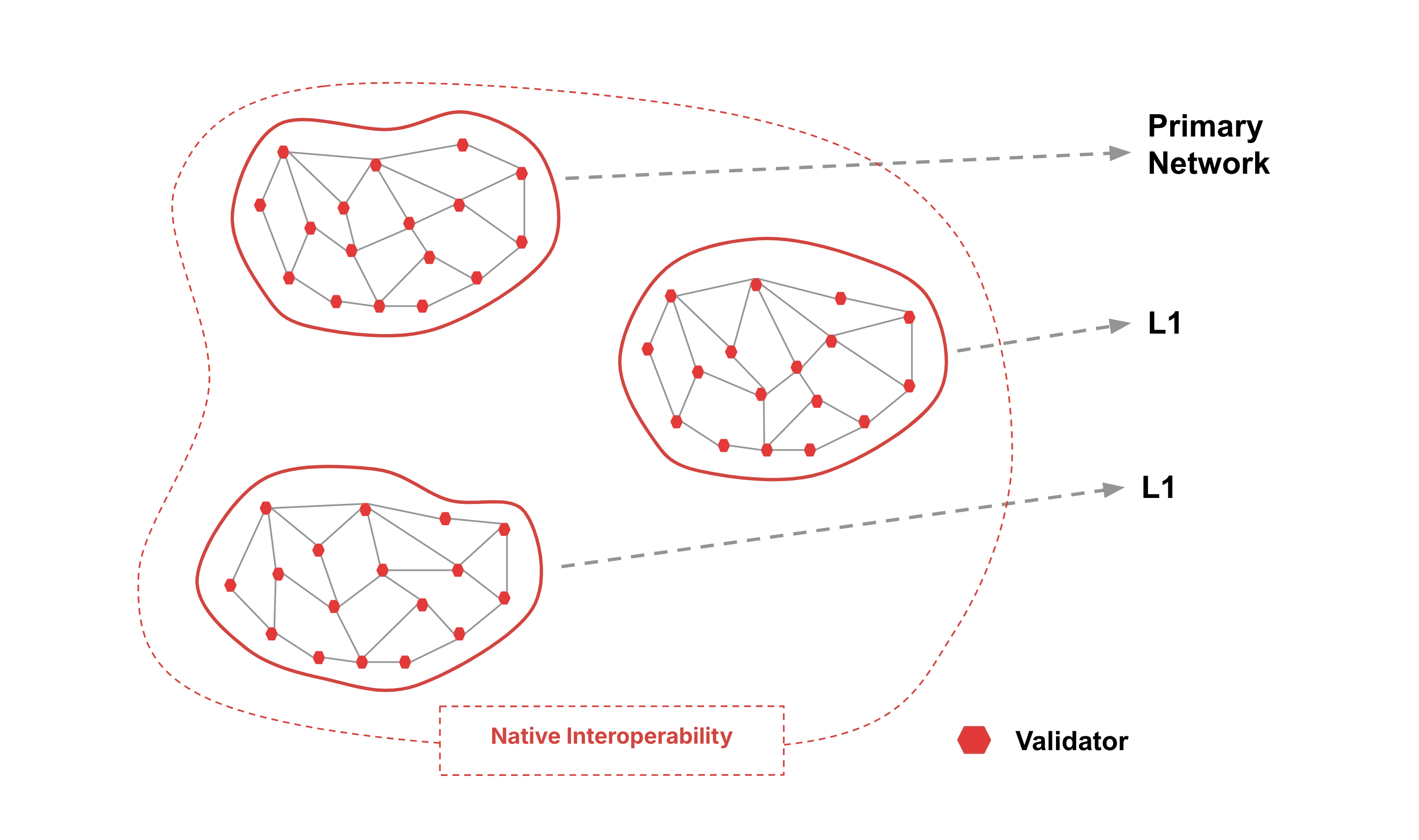
Validators in a Multi-Chain Network
Validators are nodes of a blockchain that secure the network by validating the transactions.
Each L1 in the Avalanche network has it's own set of validators that is running the AvalancheGo client.
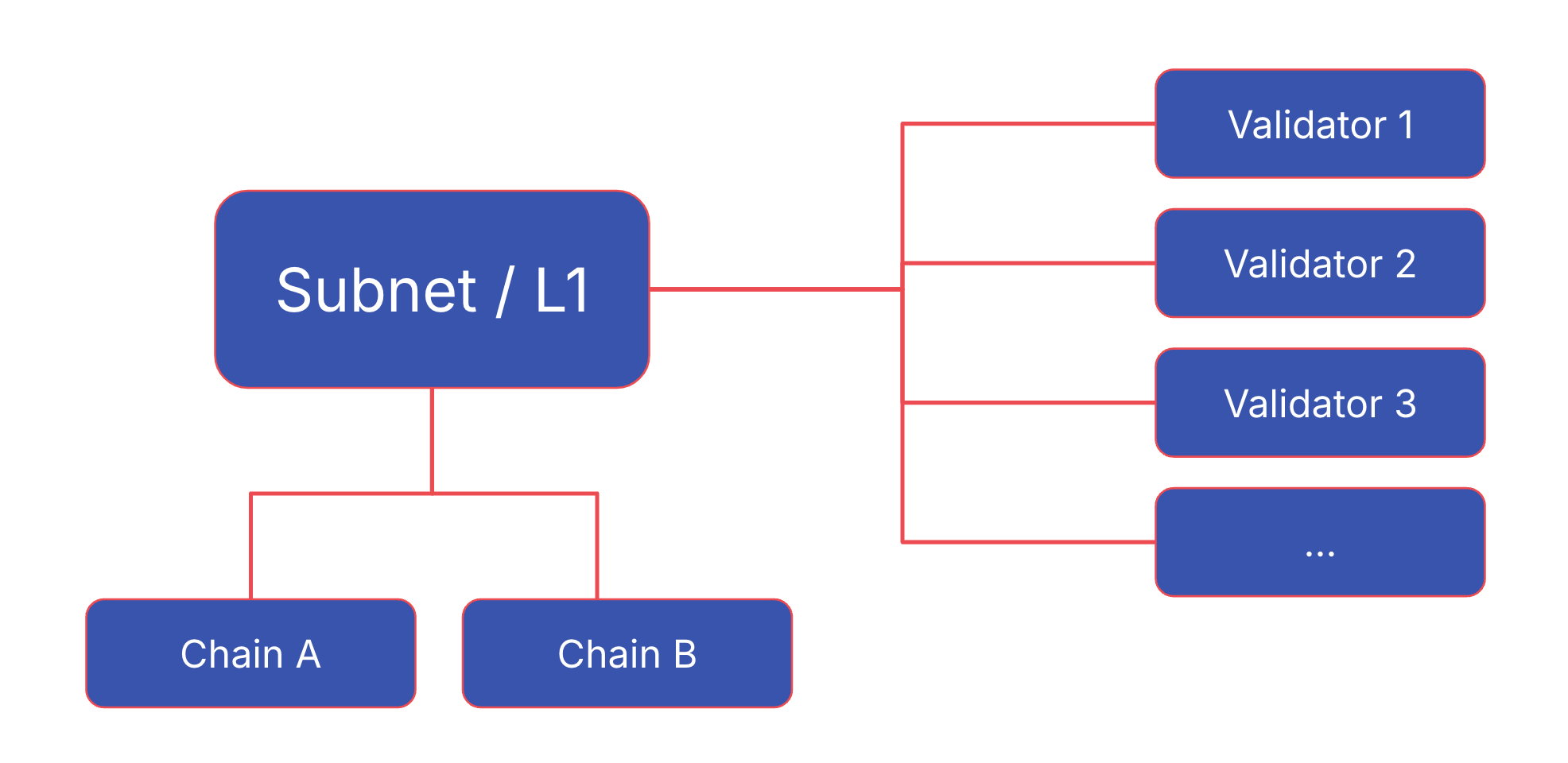
All validators are registered on the P-Chain with a unique node ID, public key, and stake weight, mapped to the blockchain they are validating.
Platform Chain
The Platform Chain is the backbone for the native interoperability of the Avalanche network. It is a registry of all validators in the Avalanche network. This includes the validators of the Primary Network (including the C- and P-Chain), as well as all L1s and legacy Subnet validators. The following graphic shows a simplified data model of the P-Chain:
Builders can create new L1 blockchains in the Avalanche Network by issuing transactions on the
P-Chain. The P-Chain runs a special-purpose virtual machine called the
platformvm. It is not
EVM-based and therefore to interact with it you need a compatible wallet like Core wallet. Creating
new records for L1 blockchains on the P-Chain is done by issuing transactions like the CreateSubnetTx.
The P-Chain is secured by the Primary Network validators. L1 validators are syncing the P-Chain, meaning they always have the latest view of the validator set of all blockchains in the Avalanche network, but are not participating in the consensus of the P-Chain.
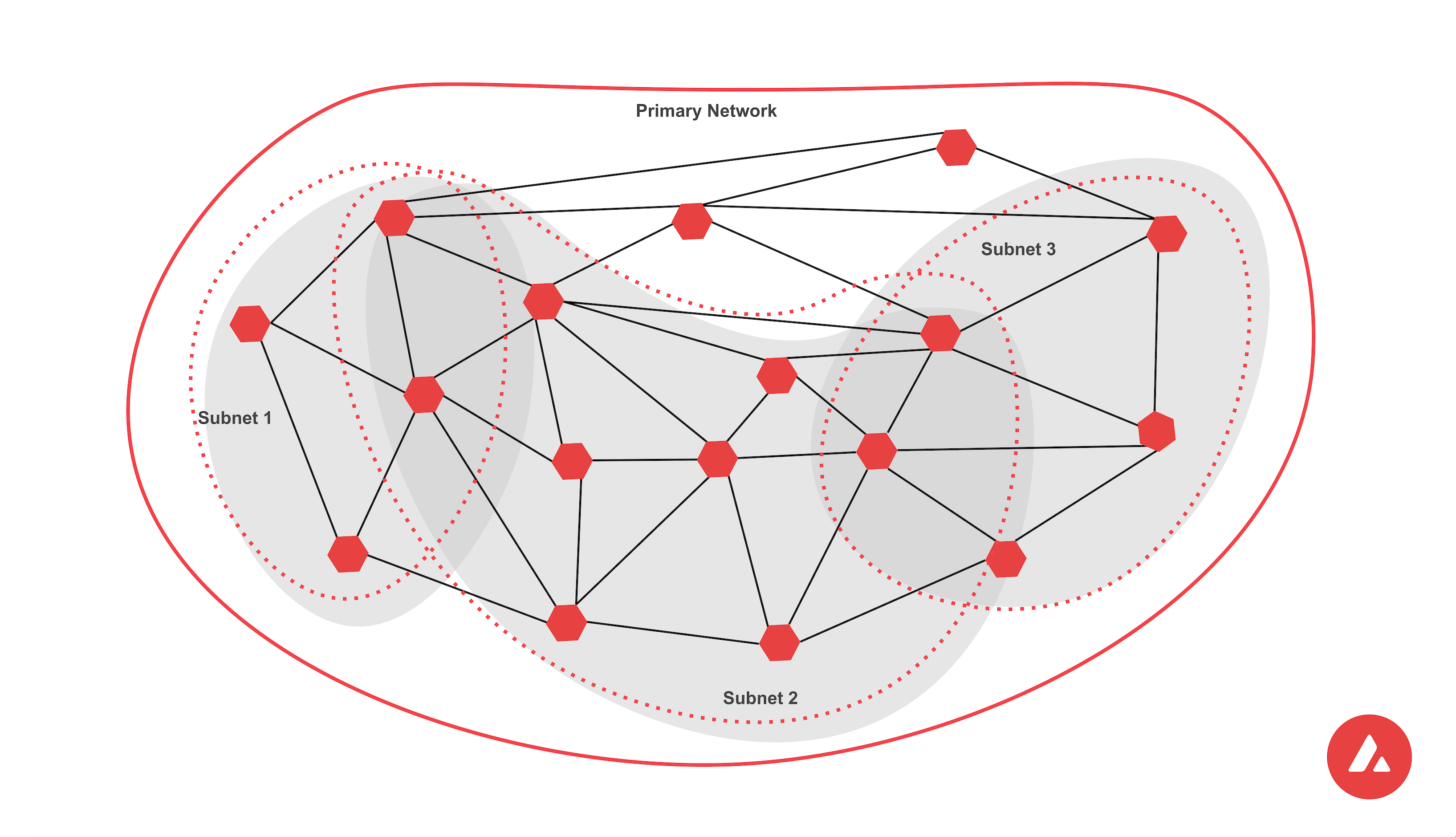
Subnets
When the Avalanche network was created the architecture included the concepts of Subnets. Subnets
are blockchains that were validated by a subset of the Primary Network validators. Each Primary
Network validator can be a member of multiple subnets, and each Subnet can have multiple validators.
Since Primary network validators have to fullfil the Primary Network staking requirements of
2,000 AVAX, this was also necessary for every validator that was validating a Subnet. There was no
option to opt-out of validating the Primary Network.
L1s
In the Avalanche9000 upgrade the concept of L1s was introduced, massively changing the architecture. Instead of having a subset of the Primary Network validators validating a Subnet, each L1 has it's own set of validators. This architecture has many advantages:
- Lower economic barrier: Validators of an L1 don't have to stake 2,000 AVAX
- Fault Tolerance: Issues on the Primary Network or L1s don't affect each other
- Running Costs: L1 Validators can be run on cheaper hardware, since they dont have to validate the Primary Network
While the concept of Subnets is still supported in the Avalanche network, it is recommended to launch new blockchains as L1s to take advantage of the benefits outlined above.
L1s are blockchains with a sovereign validator set that is registered on the P-Chain. To create an L1 you need to follow these steps:
- Create a Subnet record on the P-Chain with the
CreateSubnettransaction - Add one or more chains to the Subnet with the
CreateChaintransaction - Convert the Subnet to an L1 with the
ConvertSubnetToL1transaction
This process is very straight forward and only take one minute as you will see in this course.
Is this guide helpful?

