ICM, ICM Contracts & ICTT
Learn how Avalanche implements secure interoperability with ICM, ICM Contracts (Teleporter), and ICTT
We can look at Avalanche's Native Interoperability with a layered approach, each step guaranteeing that our message is securely sent across systems.
In order to understand the fundamentals of cross-chain messaging, here are 5 concepts that we will be covering in this chapter that make it possible:
- Secure Signatures - The foundation that ensures messages can be trusted
- ICM (Interchain Messaging) - Native blockchain feature that enables cross-chain communication
- ICM Contracts - Developer-friendly tools that make building cross-chain apps easier
- ICTT (Interchain Token Transfer) - Ready-to-use solution for moving tokens between chains (not always used)
- Relayers - service that helps deliver messages between chains by collecting signatures and submitting transactions

Knowing the components is the first piece of the puzzle, grasping how they interact with each other is the next step. In the next image we can see
Interchain Messaging (ICM)
ICM is the foundation of cross-chain communication on Avalanche. It's built directly into every Avalanche blockchain, making it a native feature rather than an add-on.
What ICM Does
Think of ICM as a built-in postal system for blockchains:
- Creates Messages: Smart contracts can create messages to send to other blockchains
- Signs Messages: Validators sign these messages to prove they're authentic
- Verifies Messages: Destination blockchains can verify that messages are genuine
The Warp Precompile
At the heart of ICM is the "warp precompile" - a special smart contract that comes pre-installed on every Avalanche blockchain. Unlike regular smart contracts that developers deploy, this one is built into the blockchain software itself (and is written in go unlike most smart contracts that are in solidity).
Simple Message Flow
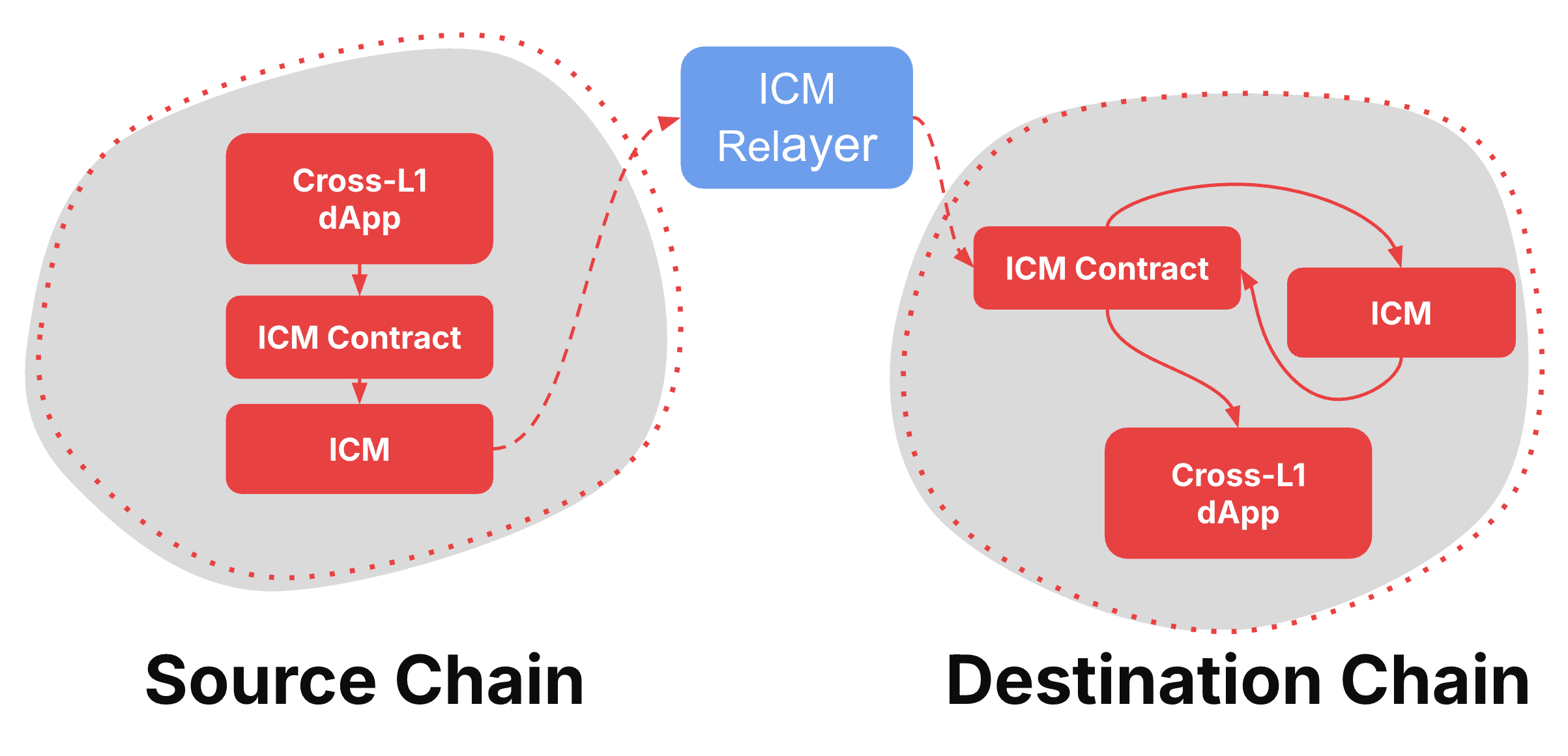
- A smart contract creates a message using the warp precompile
- The blockchain emits an event saying "I have a message to send"
- Validators sign this message to prove it's legitimate
- A relayer picks up the message and signatures
- The relayer delivers everything to the destination blockchain
- The destination blockchain verifies the signatures and accepts the message
ICM Contracts (Teleporter)
While ICM provides the basic messaging capability, developers need an easier way to use it. That's where ICM Contracts come in - specifically a contract called "Teleporter".
What Teleporter Does
Teleporter is like a user-friendly interface for ICM:
- Simple Functions: Instead of complex operations, developers just call
sendCrossChainMessage() - Message Management: Automatically handles encoding, tracking, and delivering messages
- Fee Handling: Manages payments to relayers for delivering messages
- Security: Prevents messages from being delivered twice or replayed
Why Developers Use Teleporter
- It's deployed at the same address on every blockchain
- It handles all the complex parts of cross-chain messaging
- It provides a standard way for contracts to communicate across chains
- It makes building cross-chain applications much simpler
Relayers
Relayers are the delivery service of the cross-chain messaging system. They're responsible for physically moving messages from one blockchain to another.
What Relayers Do
- Monitor Blockchains: Watch for new cross-chain messages
- Collect Signatures: Gather validator signatures that prove a message is valid
- Submit Transactions: Create and submit the transaction on the destination blockchain
- Pay Gas Fees: Cover the transaction costs on the destination chain (and get reimbursed)
Key Points About Relayers
- Anyone can run a relayer - it's permissionless
- Relayers need wallets with tokens on destination chains to pay for gas
- They can be configured to handle specific routes or all messages
- They're incentivized through fee mechanisms built into Teleporter
ICTT: An Example Cross-Chain Application
ICTT (Interchain Token Transfer) is not a core component of cross-chain messaging - it's an application built on top of ICM, Teleporter, and relayers. Think of it as one of many possible cross-chain applications.
What ICTT Does
ICTT is a pre-built solution specifically for moving tokens between blockchains:
- Token Home: Manages the original tokens on their native blockchain
- Token Remote: Creates wrapped versions of tokens on other blockchains
- Transfer Logic: Handles locking, minting, burning, and releasing tokens
Why ICTT is Special
While anyone could build their own token bridge using ICM and Teleporter, ICTT provides:
- A tested, secure implementation
- Standard contracts that work the same way everywhere
- Support for both native tokens and ERC-20 tokens
- Advanced features like "send and call" for composability
Think of ICTT like a pre-built e-commerce platform - you could build your own, but using the existing solution saves time and reduces risk.
Summary
Avalanche's cross-chain messaging system works like a well-coordinated postal service:
The Core Components:
- ICM: The built-in messaging system in every blockchain
- ICM Contracts (Teleporter): The easy-to-use interface for developers
- Relayers: The delivery service that moves messages between chains
Why It Works So Well:
- Trust: Messages are secured by the same validators that run the blockchains
- Simplicity: Developers can send messages with just a function call
- Flexibility: Anyone can build cross-chain applications (like ICTT for tokens)
- Speed: Messages are delivered in seconds, not minutes or hours
This design means developers can focus on building their applications instead of worrying about the complex infrastructure of cross-chain communication.
What Powers This System?
Now that we understand how messages travel from one blockchain to another, you might wonder: what makes this system secure? How do we know a message really came from the source blockchain and hasn't been tampered with?
The answer lies in cryptographic signatures - the digital equivalent of a tamper-proof seal. In the next sections, we'll explore:
- How validators create these digital signatures
- Why multiple signatures make the system secure
- How signatures can be efficiently combined and verified
Understanding these concepts will complete your knowledge of how Avalanche achieves secure, native interoperability.
For hands-on practice with cross-chain messaging, check out the Academy Interchain Messaging course.
Is this guide helpful?


