Account Balances & Transfers
Learn about account balances, which reflect the current amount of money or assets in an account after credits and debits. Discover how transfers work by moving funds between accounts, ensuring balance integrity across financial systems.
Account Balances
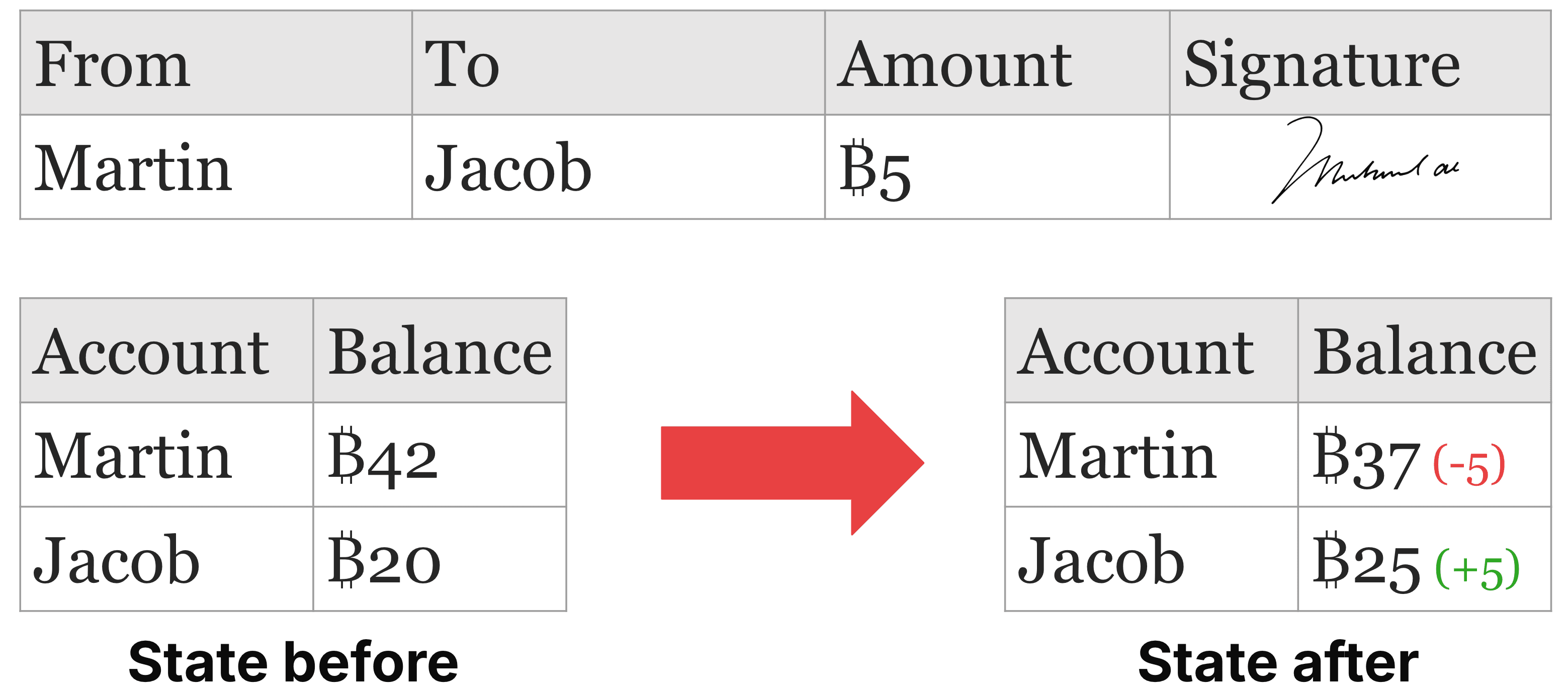
Account Balances refer to the current amount of money or assets held in a specific account at a given time. This number reflects the total value after all credits (additions) and debits (subtractions) have been accounted for, indicating how much the account holder has available to use or withdraw. For example, in a bank account, the balance represents the amount of money that the account holder can access, whether for spending, saving, or transferring.

Transfers
A Transfer is the process of moving money or assets from one account to another. During a transfer, the balance of the sending account is reduced by the amount being transferred, while the balance of the receiving account is increased by the same amount. This operation ensures that the total value across all accounts remains constant, maintaining the integrity of the overall financial system.
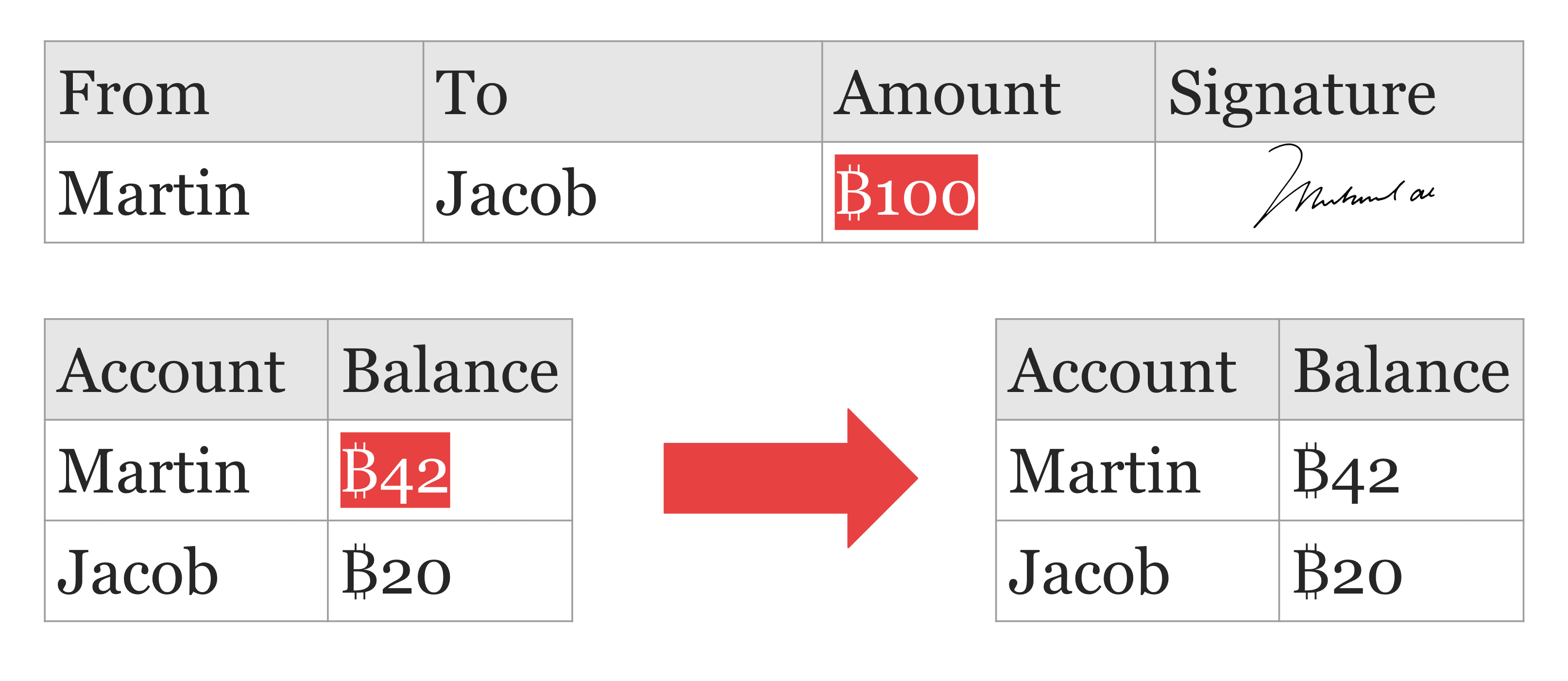
Invalid Transfers
An invalid transfer occurs when a transaction request exceeds the available balance in the sending account. In such cases, the transfer cannot be executed, and the system will reject the transaction to prevent overdrafts. As a result, both the sending and receiving account balances remain unchanged, preserving the integrity of the financial records. This safeguard ensures that accounts do not inadvertently fall into negative balances and maintains accurate and reliable financial tracking.
Is this guide helpful?
Payments Use Case
Explore how blockchain technology can revolutionize payments by building decentralized systems. This chapter delves into account balances, transactions, and user interactions, highlighting the benefits of blockchain for security, transparency, and decentralization. Discover how these concepts apply to various use cases beyond payments, including decentralized finance, voting systems, and supply chain management.
Ledger
Understand the high-level structure of this chapter.


